Dust storms from space have intrigued scientists and space enthusiasts alike for decades. These cosmic events involve the movement of microscopic particles through the vast expanse of the universe, impacting celestial bodies in ways we are only beginning to understand. The study of these phenomena offers profound insights into the origins of our solar system and the intricate processes occurring in outer space.
The concept of dust storms from space may seem abstract to many, but its implications are far-reaching. Cosmic dust plays a critical role in the formation of stars, planets, and even life itself. By exploring this phenomenon, we can unravel the mysteries of the universe and enhance our understanding of how cosmic dust influences planetary systems.
This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of dust storms from space, covering everything from their origins and characteristics to their effects on Earth and other celestial bodies. Whether you're a scientist, a student, or simply a curious reader, this guide will offer valuable insights into the fascinating world of cosmic dust.
Read also:Dig N Play The Ultimate Family Entertainment Destination
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Dust Storms from Space
- Origins of Cosmic Dust
- Characteristics of Dust Storms from Space
- Effects on Celestial Bodies
- Detection and Measurement
- Scientific Research on Cosmic Dust
- Historical Observations
- Future Implications
- Technological Advancements
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to Dust Storms from Space
The phenomenon of dust storms from space is a captivating area of study that combines elements of astrophysics, geology, and meteorology. Cosmic dust, often referred to as interstellar dust, consists of tiny particles that originate from various celestial events such as supernovae, star formation, and asteroid collisions. These particles travel through space, sometimes forming vast clouds that can affect entire planetary systems.
Understanding the behavior of dust storms from space is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, they provide valuable information about the composition and evolution of our universe. Secondly, they influence the climate and atmospheric conditions of planets, including Earth. Lastly, studying these phenomena helps scientists predict potential risks and opportunities for future space exploration missions.
Origins of Cosmic Dust
Cosmic dust originates from a variety of sources, each contributing to the rich tapestry of particles found in space. The primary sources include:
- Supernovae: Explosive stellar events that release massive amounts of dust into the interstellar medium.
- Star Formation: During the early stages of star formation, dust particles coalesce to form protoplanetary disks.
- Asteroid Collisions: Collisions between asteroids produce debris that can travel vast distances through space.
- Comets: As comets approach the Sun, they release dust particles that contribute to the interplanetary dust cloud.
According to NASA, approximately 40,000 tons of cosmic dust enter Earth's atmosphere annually, providing scientists with a wealth of data to analyze and study.
Characteristics of Dust Storms from Space
Dust storms from space exhibit unique characteristics that distinguish them from terrestrial dust storms. These include:
- Size and Composition: Cosmic dust particles range in size from a few nanometers to several micrometers and are composed primarily of silicates, carbon, and iron.
- Velocity: These particles travel at incredible speeds, often exceeding 20 km/s, making them highly energetic.
- Interstellar Medium Interaction: Cosmic dust interacts with the interstellar medium, influencing the formation of new stars and planets.
Research conducted by the European Space Agency (ESA) highlights the importance of studying these characteristics to better understand the dynamics of cosmic dust storms.
Read also:Biff Buzbys Backyard The Ultimate Guide To Fun And Adventure
Effects on Celestial Bodies
Impact on Earth
Earth is not immune to the effects of dust storms from space. Cosmic dust particles entering the atmosphere can influence climate patterns, contribute to cloud formation, and even affect global temperatures. Studies have shown that these particles play a role in moderating Earth's climate by reflecting sunlight and trapping heat.
Furthermore, the deposition of cosmic dust on Earth's surface can enrich soil with essential minerals, promoting plant growth and biodiversity. This phenomenon has been observed in regions such as the Amazon rainforest, where dust from the Sahara Desert contributes to soil fertility.
Impact on Other Planets
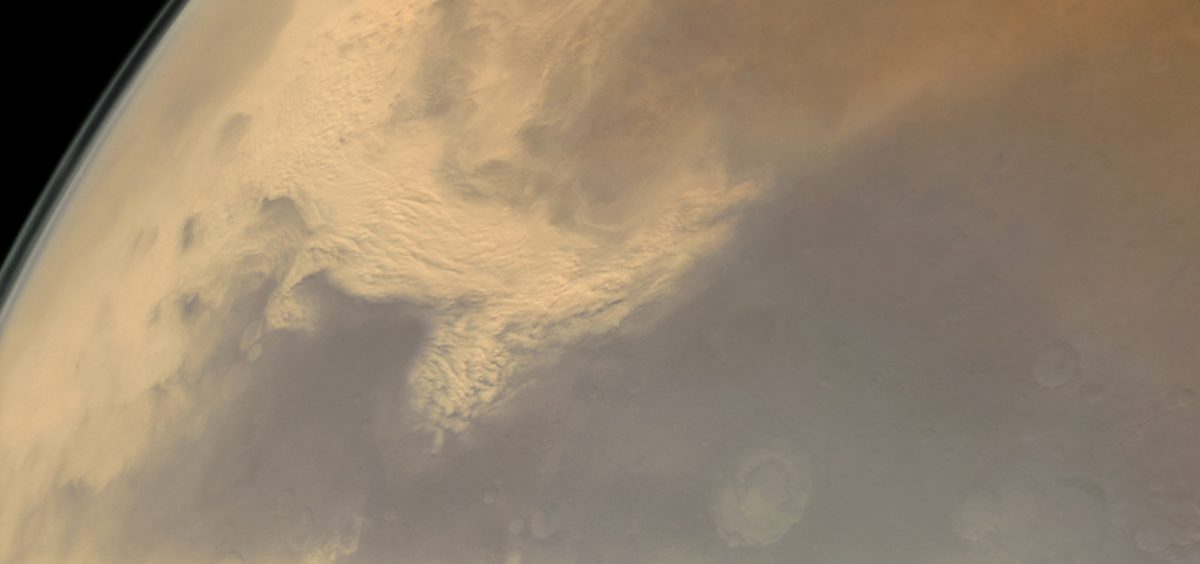
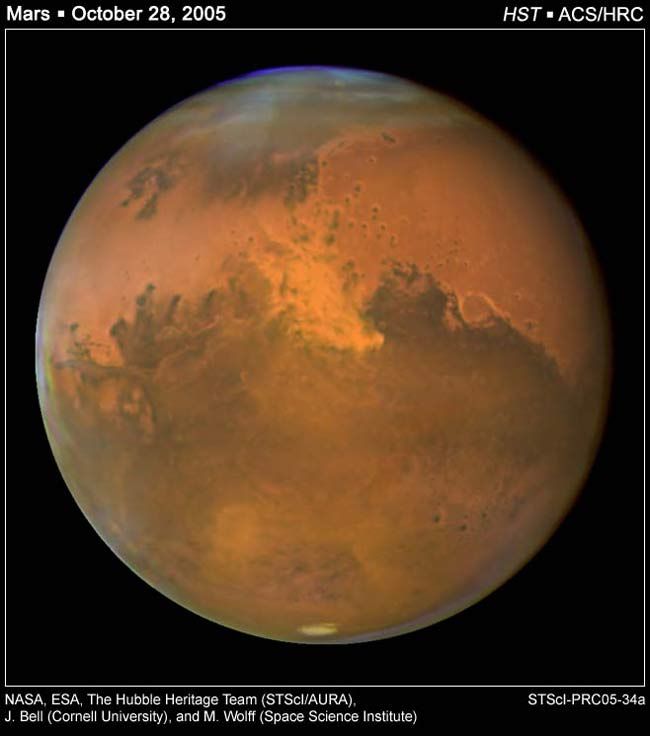
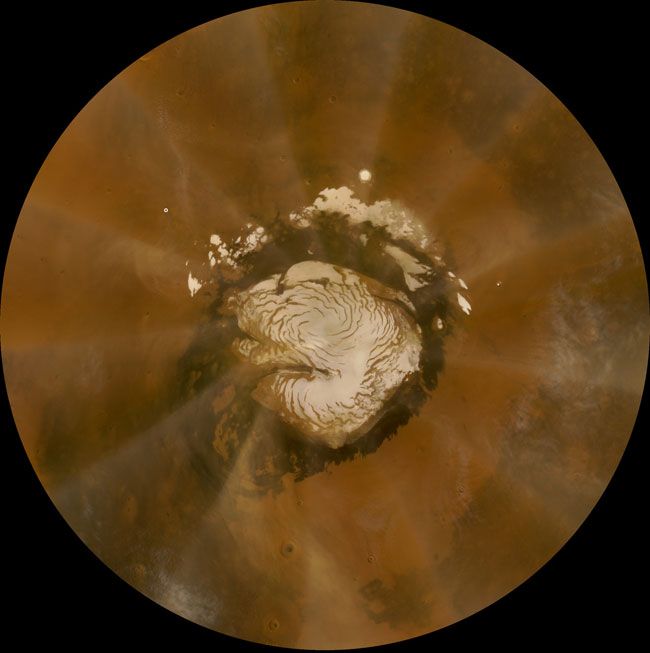
Other planets in our solar system also experience the effects of dust storms from space. Mars, for example, is known for its massive dust storms that can envelop the entire planet. These storms are fueled by cosmic dust particles that interact with the Martian atmosphere, creating complex weather patterns.
Similarly, Saturn's rings are composed largely of cosmic dust, providing scientists with valuable insights into the planet's geological history. By studying these phenomena, researchers can better understand the processes shaping our solar system.
Detection and Measurement
Detecting and measuring dust storms from space requires advanced technology and sophisticated instruments. Scientists use a variety of methods to study cosmic dust, including:
- Satellite Observations: Satellites equipped with dust detectors provide real-time data on cosmic dust distribution and movement.
- Ground-Based Telescopes: Telescopes with specialized filters can detect the presence of cosmic dust in the atmosphere.
- Space Probes: Missions such as NASA's Stardust and ESA's Rosetta have collected and analyzed cosmic dust samples, offering unprecedented insights into their composition.
These methods allow scientists to gather comprehensive data on cosmic dust, advancing our understanding of its role in the universe.
Scientific Research on Cosmic Dust
Scientific research on cosmic dust has made significant strides in recent years, thanks to advancements in technology and international collaboration. Key areas of focus include:
- Origins and Evolution: Investigating the formation and evolution of cosmic dust particles over time.
- Climate Impact: Studying the effects of cosmic dust on Earth's climate and atmospheric conditions.
- Space Exploration: Assessing the risks and opportunities associated with cosmic dust for future space missions.
Publications in reputable journals such as Nature and Science frequently highlight groundbreaking discoveries in this field, underscoring the importance of continued research.
Historical Observations
The study of dust storms from space dates back centuries, with early astronomers noting the presence of cosmic dust in the night sky. Historical observations include:
- Comet Tails: Early astronomers observed the tails of comets, which are composed largely of cosmic dust.
- Zodiacal Light: This faint glow visible in the night sky is caused by sunlight reflecting off cosmic dust particles.
- Meteor Showers: These events occur when Earth passes through streams of cosmic dust left behind by comets and asteroids.
These observations laid the foundation for modern research on cosmic dust, highlighting its significance in the study of the universe.
Future Implications
The future implications of studying dust storms from space are vast and varied. As we continue to explore the cosmos, understanding the role of cosmic dust will become increasingly important. Potential applications include:
- Climate Modeling: Incorporating cosmic dust data into climate models to improve predictions and mitigate climate change.
- Spacecraft Design: Developing materials and technologies to protect spacecraft from the effects of cosmic dust.
- Exoplanet Research: Investigating the role of cosmic dust in the formation and habitability of exoplanets.
By advancing our knowledge of cosmic dust, we can unlock new opportunities for scientific discovery and technological innovation.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have revolutionized the study of dust storms from space, enabling scientists to gather more accurate and detailed data than ever before. Key innovations include:
- Space Telescopes: Instruments like the Hubble Space Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope provide high-resolution images of cosmic dust clouds.
- Dust Detectors: Advanced sensors and detectors allow for precise measurement of cosmic dust particles in space.
- Computer Simulations: Sophisticated models simulate the behavior of cosmic dust, aiding in the interpretation of observational data.
These advancements have transformed the field of astrophysics, opening new avenues for research and exploration.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, the study of dust storms from space offers profound insights into the workings of the universe. From their origins and characteristics to their effects on celestial bodies, cosmic dust plays a critical role in shaping our understanding of the cosmos. By continuing to research and explore this fascinating phenomenon, we can unlock new knowledge and opportunities for future generations.
We invite you to join the conversation by leaving a comment below or sharing this article with others who share your passion for space exploration. Together, we can continue to advance our understanding of the universe and the incredible phenomena it holds.